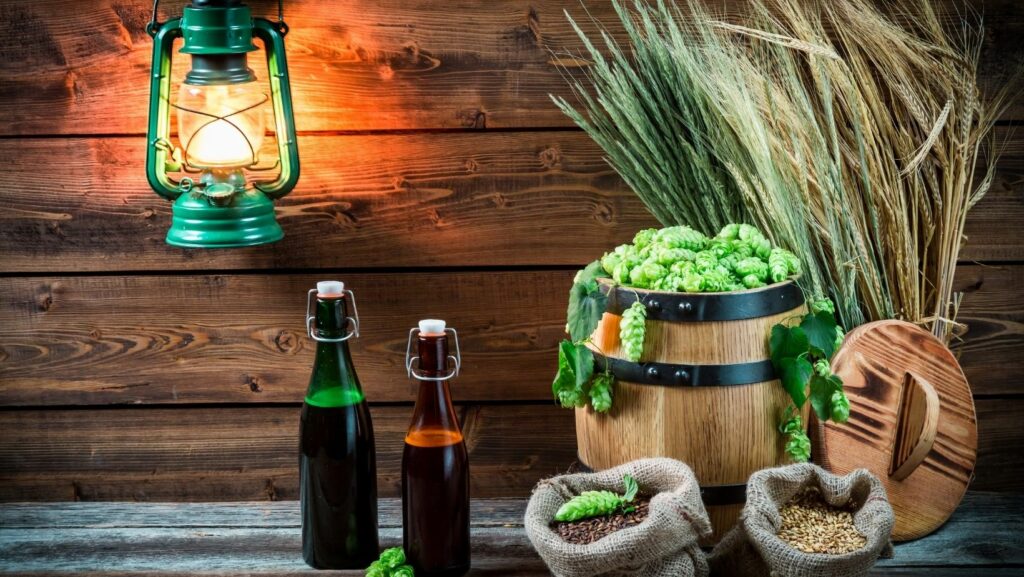
Crafting the perfect pint of beer is an art form that intertwines tradition with innovation. From selecting the finest ingredients to mastering the brewing process, beer enthusiasts delve into a world where science meets creativity. Understanding the nuances of beer brewing techniques can elevate a simple hobby into a passion for creating unique and flavorful brews. Exploring the diverse methods of brewing, from the classic to the cutting-edge, opens doors to endless possibilities for crafting distinct flavors and aromas. Whether it’s the precise temperature control during fermentation or the art of dry hopping for that extra burst of flavor, each technique plays a crucial role in shaping the final product.
Crafting the perfect pint of beer is an art form that intertwines tradition with innovation. From selecting the finest ingredients to mastering the brewing process, beer enthusiasts delve into a world where science meets creativity. Understanding the nuances of beer brewing techniques can elevate a simple hobby into a passion for creating unique and flavorful brews. Exploring the diverse methods of brewing, from the classic to the cutting-edge, opens doors to endless possibilities for crafting distinct flavors and aromas. Whether it’s the precise temperature control during fermentation or the art of dry hopping for that extra burst of flavor, each technique plays a crucial role in shaping the final product.
Beer Brewing Techniques
Exploring a myriad of beer brewing techniques adds depth and complexity to the craft. Each method offers a distinct set of advantages, allowing brewers to experiment and create diverse flavors that cater to different palates. Below are some key beer brewing techniques that encompass both traditional practices and innovative approaches:
1. All-Grain Brewing
All-grain brewing involves using malted grains as the primary source of fermentable sugars. Brewers crush the grains themselves, extracting sugars through a mashing process that occurs at specific temperatures. This method provides greater control over the beer’s flavor profile and is favored by those seeking to customize their brews extensively.
2. Extract Brewing
 Extract brewing simplifies the brewing process by utilizing malt extracts instead of whole grains. It is a popular technique among beginners or those with time constraints. While it offers less flexibility in flavor manipulation compared to all-grain brewing, extract brewing can still yield excellent results with a wide range of available extract types. Lagering is a technique primarily associated with lager beer production, involving a cold fermentation and conditioning process. This method requires patience as the beer ferments at lower temperatures for an extended period. The resulting lagers are known for their crisp, clean profiles, making lagering a crucial technique for achieving a specific beer style.
Extract brewing simplifies the brewing process by utilizing malt extracts instead of whole grains. It is a popular technique among beginners or those with time constraints. While it offers less flexibility in flavor manipulation compared to all-grain brewing, extract brewing can still yield excellent results with a wide range of available extract types. Lagering is a technique primarily associated with lager beer production, involving a cold fermentation and conditioning process. This method requires patience as the beer ferments at lower temperatures for an extended period. The resulting lagers are known for their crisp, clean profiles, making lagering a crucial technique for achieving a specific beer style.
3. Dry Hopping
Dry hopping is a modern brewing technique that involves adding hops directly to the fermenting or aging beer to enhance its aroma and flavor. This method does not contribute significantly to the beer’s bitterness but imparts floral, citrusy, or fruity notes. Brewers often use dry hopping to elevate the sensory experience of their brews, especially in hop-forward beer styles like IPAs.
Achieving Optimal Boiling and Hopping
 Building on the precision and experimentation in beer brewing, achieving optimal boiling and hopping plays a crucial role in developing distinct flavors and aromas. The boiling process is essential for extracting bitterness, flavor, and aroma from hops, while hopping involves the deliberate addition of hops at various stages to balance a beer’s taste profile. Dry hopping involves adding hops directly to the fermenter after primary fermentation to boost aroma without increasing bitterness. It’s a popular method for imparting floral, citrus, or piney notes to the beer, enhancing its overall sensory experience. Boiling the wort at the right temperature, typically around 212°F (100°C), is vital to extract alpha acids from hops effectively. Consistent boiling for about 60-90 minutes enables the enzymes to break down proteins, leading to better clarity and stability in the final beer.
Building on the precision and experimentation in beer brewing, achieving optimal boiling and hopping plays a crucial role in developing distinct flavors and aromas. The boiling process is essential for extracting bitterness, flavor, and aroma from hops, while hopping involves the deliberate addition of hops at various stages to balance a beer’s taste profile. Dry hopping involves adding hops directly to the fermenter after primary fermentation to boost aroma without increasing bitterness. It’s a popular method for imparting floral, citrus, or piney notes to the beer, enhancing its overall sensory experience. Boiling the wort at the right temperature, typically around 212°F (100°C), is vital to extract alpha acids from hops effectively. Consistent boiling for about 60-90 minutes enables the enzymes to break down proteins, leading to better clarity and stability in the final beer.
- Hop Additions:
- Bittering Hops: Added at the beginning of the boil, these hops contribute bitterness to the beer.
- Flavor Hops: Added towards the middle of the boil, these hops provide flavor characteristics.
- Aroma Hops: Added towards the end of the boil or during fermentation, these hops enhance the beer’s aroma without adding significant bitterness.
By mastering the art of optimal boiling and hopping techniques, brewers can craft beers with complex flavor profiles, balanced bitterness, and enticing aromas, showcasing their expertise and passion for creating exceptional brews.